Porcupine notation: Difference between revisions
m Added to category "notation" |
m Text replacement - "Ups_and_Downs_Notation" to "Ups and downs notation" |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[ | [[Mike Battaglia]] posted the following description of a [[Porcupine]] notation to the Xenharmonic Alliance Facebook Group: | ||
=='' | == ''This is Paul's (and Herman's?) porcupine naming system which names the notes like this:'' == | ||
''A B C D E F G H A'' | |||
'' | ''LLLLLLLs - porcupine[8]'' | ||
'' | ''You can see that A-H consist of a chain of notes which are all 10/9 apart; B is a 10/9 generator above A, C is a 10/9 generator above B and so on. You don't have to use all those notes, though. If you only use notes A-G, you get this scale:'' | ||
'' | ''A B C D E F G A'' | ||
'' | ''ssssssL - porcupine[7]'' | ||
'' | ''Or, in terms of modes that you're familiar with'' | ||
'' | ''G H A B C D E F G'' | ||
'' | ''LsLLLLLL - porcupine[8]'' | ||
'' | ''G A B C D E F G'' | ||
'' | ''Lssssss'' | ||
'' | ''Therefore, you can see that picking this 8-note naming system for porcupine[8] gives you a 7-note naming for porcupine[7] automatically, by default.'' | ||
'' | ''Let's say we want to play around in porcupine[7]. What we need now is an accidental to represent the porcupine[7] chroma. Since the chroma for porcupine[7] is about a quarter tone, I'll use ^/v for that. (My reasons for not using #/b will become clear below). Therefore, observe'' | ||
'' | ''G A B C D E F G - porcupine[7] Lssssss'' | ||
'' | ''G A B Cv D E F^ G - JI major scale as a MODMOS of porcupine[7]'' | ||
'' | ''G A B C D E Fv G - awesome otonal major scale everyone should use'' | ||
'' | ''G Av B C D E F G - porcupine[7] sLsssss'' | ||
'' | ''G B D - major'' | ||
'' | ''G Bv D - minor'' | ||
'' | ''OK, great. But now let's say we want to actually use those 8 notes, and throw H back in as the note that's one 10/9 generator above "G." Now what? Well, we need a chroma for that too then, one which represents L-s in porcupine[8]. Since this chroma is more like the size of a "half step," I'll use #/b for it.'' | ||
'' | ''So then we get'' | ||
'' | ''G H A B C D E F G - porcupine[8] LsLLLLLL'' | ||
'' | ''G Hb A B C D E F G - porcupine[8] sLLLLLLL'' | ||
'' | ''G H A# B C D E F G - porcupine[8] LLsLLLLL'' | ||
'' | ''etc. OK, you get it.'' | ||
'' | ''The interesting thing is that H is the same note as Av, and Hb is the same note as G^, and A# is the same note as Bv, and so on. In other words, you end up with different options as to how you want to enharmonically spell notes. So you can use porcupine[7] if you want, and use the A-G nominals, and pick an accidental for your chroma, and everything will work fine. And then if you want to use porcupine[8] you can just add "H" in there as one generator above "G", and pick a porcupine[8] chroma, and everything will still work fine.'' | ||
'' | ''You can even switch between the two like Igs was suggesting, and you'll find that every pitch which could ever possibly appear in the porcupine tuning system can be indexed by either one of the two notational systems. You can even use the porcupine[7] chroma over porcupine[8] names if you want and so on (but be careful notationally, it's easy to run into trouble - in the scale G H Av B C D E F G, H and Av are the same thing!).'' | ||
'' | '' I think this is a pretty natural way to do things if you want to use both porcupine[7] and porcupine[8].'' | ||
~ ~ ~ | |||
[[Paul_Erlich|Paul Erlich]] commented: ''I didn't come up with it but I like it because each of the four consonant triads in porcupine-7 gets a conventional spellings for its quality. D-F-A and E-G-B are minor, and F-A-C and G-B-D are major. Also the minor seventh chords D-F-A-C and E-G-B-D.'' | |||
''~ ~ ~'' | |||
Mike added: | |||
''BTW with this notation system, one question is - how many lines do you use in a staff? I guess you'd have to have "staff switches" in the middle of a score if you want to switch into a porcupine[8]-oriented notation or what have you. ... Actually, forget staff changes, why not clef changes? 5 lines can accommodate 1 octave of both porcupine[7] and porcupine[8], so there you go.'' | |||
'' | ''~ ~ ~'' | ||
== William Lynch's Approach == | |||
William Lynch generally likes to reinvent the wheel. He proposed a system of notation for 15 EDO based on porcupine[8] as the fundamental scale. | William Lynch generally likes to reinvent the wheel. He proposed a system of notation for 15 EDO based on porcupine[8] as the fundamental scale. | ||
| Line 86: | Line 85: | ||
[[File:porcupine_circles_22edo.png|alt=porcupine circles 22edo.png|499x462px|porcupine circles 22edo.png]] | [[File:porcupine_circles_22edo.png|alt=porcupine circles 22edo.png|499x462px|porcupine circles 22edo.png]] | ||
[[File:porcupine_generator_chain.png|alt=porcupine generator chain.png|porcupine generator chain.png]] | |||
----- | ----- | ||
| Line 94: | Line 93: | ||
''Yikes, so #v (sharp-down) is 40/39 and b^^ (flat-double-up) is 65/64 -- and in a 13-limit Porcupine musical setting, unless you're in 37edo, they're not the same, and they're both necessary if you want to spell your scales logically!'' | ''Yikes, so #v (sharp-down) is 40/39 and b^^ (flat-double-up) is 65/64 -- and in a 13-limit Porcupine musical setting, unless you're in 37edo, they're not the same, and they're both necessary if you want to spell your scales logically!'' | ||
''Let's | ''Let's say you want an 8:9:10:11:12:13:14 chord with letter names A B C D E F G. If you start it on Av, it's:'' | ||
''Av B C D E Fb^ G'' | |||
'' | ''...with the flat-up turning a 5/3 into 13/8 by subtracting 40/39.'' | ||
'' | ''But if I start it on A natural, I get:'' | ||
'' | ''A B^ C^ D^ E^ Fb^^ G^'' | ||
'' | ''...with the flat-double-up turning an 8/5 into 13/8 by adding 65/64!'' | ||
'' | ''To summarize:'' | ||
'' | ''#v is the chroma in Porcupine[15].'' | ||
'' | ''In a 13-limit setting, it's 40/39.'' | ||
'' | ''In 15edo it's tempered out.'' | ||
'' | ''In 22edo, it's one degree, which would mean, for example, A#v=A^; so we don't need it to describe all the pitches.'' | ||
'' | ''In 37edo, it's one degree, but A#v != A^, because ^ is two degrees.'' | ||
'' | ''b^^ is the chroma in Porcupine[22].'' | ||
'' | ''In a 13-limit setting, it's 65/64.'' | ||
'' | ''In 15edo, it's equivalent to ^ and # and therefore totally unnecessary.'' | ||
'' | ''In 22edo, it's tempered out.'' | ||
'' | ''In 37edo, it's one degree, which means that #v and bvv are in fact the same, and only one accidental would be needed.'' | ||
'' | ''In other Porcupinefish systems (like 59edo, for instance), it's smaller than #v, and therefore needs a distinct and preferably smaller symbol.'' | ||
'' | ''That's my proposal for expanding the Porcupine notation [https://www.facebook.com/MikeBattagliaMusic Mike Battaglia] has described into the 13-limit. Does this make sense to people?'' | ||
'' | ''BTW with this notation system, one question is - how many lines do you use in a staff? I guess you'd have to have "staff switches" in the middle of a score if you want to switch into a porcupine[8]-oriented notation or what have you.'' | ||
' | == Kite Giedraitis's approach == | ||
Porcupine divides the perfect 4th into 3 equal steps, thus its [[pergen|pergen]] is (P8, P4/3). [[Ups and downs notation|Ups and downs]] [[Ups and downs notation|notation]] can be used. The generator is vM2. The enharmonic is v<span style="vertical-align: super;">3</span>A1, thus ^<span style="vertical-align: super;">3</span>C equals C#. The enharmonically equivalent alternate generator is ^^m2. The genchain is | |||
...^1 - M2 - vM3 - ^4 - P5 - vM6 - ^m7 - <u>'''P1'''</u> - vM2 - ^m3 - P4 - v5 - ^m6 - m7 - v8... | |||
In C, this would be | |||
...^C - D - vE - ^F - G - vA - ^Bb - <u>'''C'''</u> - vD - ^Eb - F - vG - ^Ab - Bb - vC... | |||
Unlike the other proposals on this page, the notes without ups and downs still form the familiar chain of 5ths ...Eb Bb F C G D A E B F# C#..., and interval arithmetic remains unchanged. Staff notation is as usual, with the addition of up and down accidentals before certain notes. | |||
Porcupine[8] in A is A vB ^C D vE ^F G vA A. Porcupine[7] would omit vA. | |||
Example comma pump, with brackets indicating an enharmonic equivalence: | |||
Cv -- vA^m -- vDv -- [vvB=^Bb]^m -- ^Ebv -- ^Abv -- Cv | |||
See the ups and downs page for an explanation of the chord names. | |||
This is the rank-2 notation, for a generator of indeterminate cents. The edo notation uses ups and downs to represent one EDO-step. If an edo tempers out porcupine, it must be sharp-3, sharp-6, sharp-9, etc. (See the scale tree on the [[EDO|EDOs]] page.) The notation is identical for sharp-3 edos (15, 22, 29, etc.). For sharp-6 edos (e.g. 30 or 72), simply double all ups and downs. The generator is vvM2. The genchain is P1 - vvM2 - ^^m3 - P4 - vv5... or C - vvD - ^^Eb - F - vvG... Sharp-9 edos are rarely used, but the generator would be v<span style="font-size: 14.4px; vertical-align: super;">3</span>M2. | |||
== Vector's approach == | |||
The notes of the porcupine zarlino scale (LH Nice-Ionian) are labelled CDEFGAB corresponding to the diatonic scale in Ionian. The porcupine chroma is then notated by sharps and flats. | |||
Intervals are given irregular "functional names", as using a non-MOS as the base scale causes intervals to behave unexpectedly. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+ | |||
!Note | |||
!Onyx (TAMNAMS) | |||
!Steps of 15edo | |||
!Steps of 22edo | |||
!Interval on C (functional name) | |||
|- | |||
|Cb | |||
|d0 | |||
|14 | |||
|21 | |||
|diminished unison/octave | |||
|- | |||
|C | |||
|P0 | |||
|0 | |||
|0 | |||
|perfect unison/octave | |||
|- | |||
|C# | |||
|A0 | |||
|1 | |||
|1 | |||
|augmented unison/octave | |||
|- | |||
|Dbb | |||
|dd1 | |||
|0 | |||
|1 | |||
|diminished second | |||
|- | |||
|Db | |||
|d1 | |||
|1 | |||
|2 | |||
|minor second | |||
|- | |||
|D | |||
|P1 | |||
|2 | |||
|3 | |||
|narrow major second | |||
|- | |||
|D# | |||
|A1 | |||
|3 | |||
|4 | |||
|wide major second | |||
|- | |||
|D## | |||
|AA1 | |||
|4 | |||
|5 | |||
|augmented second | |||
|- | |||
|E3b | |||
|dd2 | |||
|2 | |||
|4 | |||
|diminished third | |||
|- | |||
|Ebb | |||
|d2 | |||
|3 | |||
|5 | |||
|wolf third | |||
|- | |||
|Eb | |||
|m2 | |||
|4 | |||
|6 | |||
|minor third | |||
|- | |||
|E | |||
|M2 | |||
|5 | |||
|7 | |||
|major third | |||
|- | |||
|E# | |||
|A2 | |||
|6 | |||
|8 | |||
|augmented third | |||
|- | |||
|Fb | |||
|d3 | |||
|5 | |||
|8 | |||
|diminished fourth | |||
|- | |||
|F | |||
|m3 | |||
|6 | |||
|9 | |||
|perfect fourth | |||
|- | |||
|F# | |||
|M3 | |||
|7 | |||
|10 | |||
|wolf fourth | |||
|- | |||
|F## | |||
|A3 | |||
|8 | |||
|11 | |||
|augmented fourth | |||
|- | |||
|Gbb | |||
|d4 | |||
|7 | |||
|11 | |||
|diminished fifth | |||
|- | |||
|Gb | |||
|m4 | |||
|8 | |||
|12 | |||
|wolf fifth | |||
|- | |||
|G | |||
|M4 | |||
|9 | |||
|13 | |||
|perfect fifth | |||
|- | |||
|G# | |||
|A4 | |||
|10 | |||
|14 | |||
|augmented fifth | |||
|- | |||
|Abb | |||
|d5 | |||
|9 | |||
|14 | |||
|diminished sixth | |||
|- | |||
|Ab | |||
|m5 | |||
|10 | |||
|15 | |||
|minor sixth | |||
|- | |||
|A | |||
|M5 | |||
|11 | |||
|16 | |||
|major sixth | |||
|- | |||
|A# | |||
|A5 | |||
|12 | |||
|17 | |||
|wolf sixth | |||
|- | |||
|A## | |||
|AA5 | |||
|13 | |||
|18 | |||
|augmented sixth | |||
|- | |||
|B3b | |||
|dd6 | |||
|11 | |||
|17 | |||
|diminished seventh | |||
|- | |||
|Bbb | |||
|d6 | |||
|12 | |||
|18 | |||
|narrow minor seventh / harmonic seventh | |||
|- | |||
|Bb | |||
|P6 | |||
|13 | |||
|19 | |||
|wide minor seventh / dominant seventh | |||
|- | |||
|B | |||
|A6 | |||
|14 | |||
|20 | |||
|major seventh | |||
|- | |||
|B# | |||
|AA6 | |||
|0 | |||
|21 | |||
|augmented seventh | |||
|} | |||
{{Navbox notation}} | |||
[[Category:Porcupine]] | [[Category:Porcupine]] | ||
[[Category:Notation]] | [[Category:Notation]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:10, 20 August 2025
Mike Battaglia posted the following description of a Porcupine notation to the Xenharmonic Alliance Facebook Group:
This is Paul's (and Herman's?) porcupine naming system which names the notes like this:
A B C D E F G H A
LLLLLLLs - porcupine[8]
You can see that A-H consist of a chain of notes which are all 10/9 apart; B is a 10/9 generator above A, C is a 10/9 generator above B and so on. You don't have to use all those notes, though. If you only use notes A-G, you get this scale:
A B C D E F G A
ssssssL - porcupine[7]
Or, in terms of modes that you're familiar with
G H A B C D E F G
LsLLLLLL - porcupine[8]
G A B C D E F G
Lssssss
Therefore, you can see that picking this 8-note naming system for porcupine[8] gives you a 7-note naming for porcupine[7] automatically, by default.
Let's say we want to play around in porcupine[7]. What we need now is an accidental to represent the porcupine[7] chroma. Since the chroma for porcupine[7] is about a quarter tone, I'll use ^/v for that. (My reasons for not using #/b will become clear below). Therefore, observe
G A B C D E F G - porcupine[7] Lssssss
G A B Cv D E F^ G - JI major scale as a MODMOS of porcupine[7]
G A B C D E Fv G - awesome otonal major scale everyone should use
G Av B C D E F G - porcupine[7] sLsssss
G B D - major
G Bv D - minor
OK, great. But now let's say we want to actually use those 8 notes, and throw H back in as the note that's one 10/9 generator above "G." Now what? Well, we need a chroma for that too then, one which represents L-s in porcupine[8]. Since this chroma is more like the size of a "half step," I'll use #/b for it.
So then we get
G H A B C D E F G - porcupine[8] LsLLLLLL
G Hb A B C D E F G - porcupine[8] sLLLLLLL
G H A# B C D E F G - porcupine[8] LLsLLLLL
etc. OK, you get it.
The interesting thing is that H is the same note as Av, and Hb is the same note as G^, and A# is the same note as Bv, and so on. In other words, you end up with different options as to how you want to enharmonically spell notes. So you can use porcupine[7] if you want, and use the A-G nominals, and pick an accidental for your chroma, and everything will work fine. And then if you want to use porcupine[8] you can just add "H" in there as one generator above "G", and pick a porcupine[8] chroma, and everything will still work fine.
You can even switch between the two like Igs was suggesting, and you'll find that every pitch which could ever possibly appear in the porcupine tuning system can be indexed by either one of the two notational systems. You can even use the porcupine[7] chroma over porcupine[8] names if you want and so on (but be careful notationally, it's easy to run into trouble - in the scale G H Av B C D E F G, H and Av are the same thing!).
I think this is a pretty natural way to do things if you want to use both porcupine[7] and porcupine[8].
~ ~ ~
Paul Erlich commented: I didn't come up with it but I like it because each of the four consonant triads in porcupine-7 gets a conventional spellings for its quality. D-F-A and E-G-B are minor, and F-A-C and G-B-D are major. Also the minor seventh chords D-F-A-C and E-G-B-D.
~ ~ ~
Mike added:
BTW with this notation system, one question is - how many lines do you use in a staff? I guess you'd have to have "staff switches" in the middle of a score if you want to switch into a porcupine[8]-oriented notation or what have you. ... Actually, forget staff changes, why not clef changes? 5 lines can accommodate 1 octave of both porcupine[7] and porcupine[8], so there you go.
~ ~ ~
William Lynch's Approach
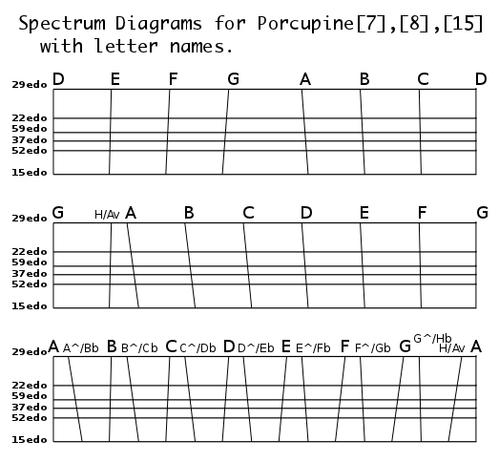
William Lynch generally likes to reinvent the wheel. He proposed a system of notation for 15 EDO based on porcupine[8] as the fundamental scale.
I think it's worthwhile to explore these scales from scratch with no previous associations. I chose this old-english based alphabet as the nominals of porcupine[8]. They work for porcupine[7] as well if you leave out "ð" from the scale.
Porcupine 8 alphabet: b c d ð e f þ æ
Porcupine 7 alphabet: b c d e f þ æ
------------
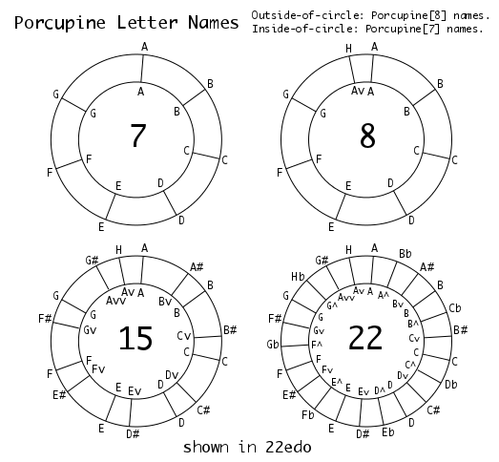
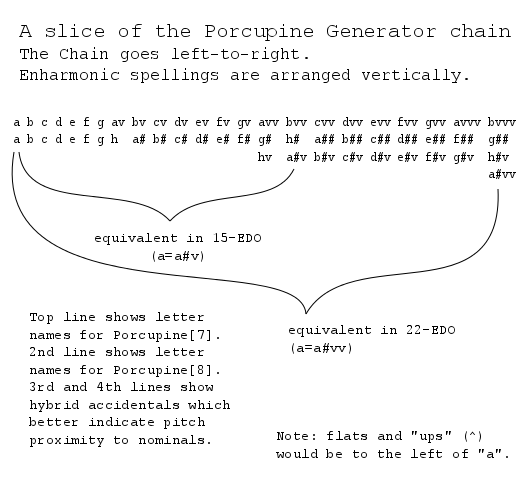
Some diagrams by Andrew Heathwaite to illustrate:
Andrew added:
Yikes, so #v (sharp-down) is 40/39 and b^^ (flat-double-up) is 65/64 -- and in a 13-limit Porcupine musical setting, unless you're in 37edo, they're not the same, and they're both necessary if you want to spell your scales logically!
Let's say you want an 8:9:10:11:12:13:14 chord with letter names A B C D E F G. If you start it on Av, it's:
Av B C D E Fb^ G
...with the flat-up turning a 5/3 into 13/8 by subtracting 40/39.
But if I start it on A natural, I get:
A B^ C^ D^ E^ Fb^^ G^
...with the flat-double-up turning an 8/5 into 13/8 by adding 65/64!
To summarize:
#v is the chroma in Porcupine[15].
In a 13-limit setting, it's 40/39.
In 15edo it's tempered out.
In 22edo, it's one degree, which would mean, for example, A#v=A^; so we don't need it to describe all the pitches.
In 37edo, it's one degree, but A#v != A^, because ^ is two degrees.
b^^ is the chroma in Porcupine[22].
In a 13-limit setting, it's 65/64.
In 15edo, it's equivalent to ^ and # and therefore totally unnecessary.
In 22edo, it's tempered out.
In 37edo, it's one degree, which means that #v and bvv are in fact the same, and only one accidental would be needed.
In other Porcupinefish systems (like 59edo, for instance), it's smaller than #v, and therefore needs a distinct and preferably smaller symbol.
That's my proposal for expanding the Porcupine notation Mike Battaglia has described into the 13-limit. Does this make sense to people?
BTW with this notation system, one question is - how many lines do you use in a staff? I guess you'd have to have "staff switches" in the middle of a score if you want to switch into a porcupine[8]-oriented notation or what have you.
Kite Giedraitis's approach
Porcupine divides the perfect 4th into 3 equal steps, thus its pergen is (P8, P4/3). Ups and downs notation can be used. The generator is vM2. The enharmonic is v3A1, thus ^3C equals C#. The enharmonically equivalent alternate generator is ^^m2. The genchain is
...^1 - M2 - vM3 - ^4 - P5 - vM6 - ^m7 - P1 - vM2 - ^m3 - P4 - v5 - ^m6 - m7 - v8...
In C, this would be
...^C - D - vE - ^F - G - vA - ^Bb - C - vD - ^Eb - F - vG - ^Ab - Bb - vC...
Unlike the other proposals on this page, the notes without ups and downs still form the familiar chain of 5ths ...Eb Bb F C G D A E B F# C#..., and interval arithmetic remains unchanged. Staff notation is as usual, with the addition of up and down accidentals before certain notes.
Porcupine[8] in A is A vB ^C D vE ^F G vA A. Porcupine[7] would omit vA.
Example comma pump, with brackets indicating an enharmonic equivalence:
Cv -- vA^m -- vDv -- [vvB=^Bb]^m -- ^Ebv -- ^Abv -- Cv
See the ups and downs page for an explanation of the chord names.
This is the rank-2 notation, for a generator of indeterminate cents. The edo notation uses ups and downs to represent one EDO-step. If an edo tempers out porcupine, it must be sharp-3, sharp-6, sharp-9, etc. (See the scale tree on the EDOs page.) The notation is identical for sharp-3 edos (15, 22, 29, etc.). For sharp-6 edos (e.g. 30 or 72), simply double all ups and downs. The generator is vvM2. The genchain is P1 - vvM2 - ^^m3 - P4 - vv5... or C - vvD - ^^Eb - F - vvG... Sharp-9 edos are rarely used, but the generator would be v3M2.
Vector's approach
The notes of the porcupine zarlino scale (LH Nice-Ionian) are labelled CDEFGAB corresponding to the diatonic scale in Ionian. The porcupine chroma is then notated by sharps and flats.
Intervals are given irregular "functional names", as using a non-MOS as the base scale causes intervals to behave unexpectedly.
| Note | Onyx (TAMNAMS) | Steps of 15edo | Steps of 22edo | Interval on C (functional name) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cb | d0 | 14 | 21 | diminished unison/octave |
| C | P0 | 0 | 0 | perfect unison/octave |
| C# | A0 | 1 | 1 | augmented unison/octave |
| Dbb | dd1 | 0 | 1 | diminished second |
| Db | d1 | 1 | 2 | minor second |
| D | P1 | 2 | 3 | narrow major second |
| D# | A1 | 3 | 4 | wide major second |
| D## | AA1 | 4 | 5 | augmented second |
| E3b | dd2 | 2 | 4 | diminished third |
| Ebb | d2 | 3 | 5 | wolf third |
| Eb | m2 | 4 | 6 | minor third |
| E | M2 | 5 | 7 | major third |
| E# | A2 | 6 | 8 | augmented third |
| Fb | d3 | 5 | 8 | diminished fourth |
| F | m3 | 6 | 9 | perfect fourth |
| F# | M3 | 7 | 10 | wolf fourth |
| F## | A3 | 8 | 11 | augmented fourth |
| Gbb | d4 | 7 | 11 | diminished fifth |
| Gb | m4 | 8 | 12 | wolf fifth |
| G | M4 | 9 | 13 | perfect fifth |
| G# | A4 | 10 | 14 | augmented fifth |
| Abb | d5 | 9 | 14 | diminished sixth |
| Ab | m5 | 10 | 15 | minor sixth |
| A | M5 | 11 | 16 | major sixth |
| A# | A5 | 12 | 17 | wolf sixth |
| A## | AA5 | 13 | 18 | augmented sixth |
| B3b | dd6 | 11 | 17 | diminished seventh |
| Bbb | d6 | 12 | 18 | narrow minor seventh / harmonic seventh |
| Bb | P6 | 13 | 19 | wide minor seventh / dominant seventh |
| B | A6 | 14 | 20 | major seventh |
| B# | AA6 | 0 | 21 | augmented seventh |
| View • Talk • EditMusical notation | |
|---|---|
| Universal | Sagittal notation |
| Just intonation | Functional Just System • Ben Johnston's notation (Johnston–Copper notation) • Helmholtz–Ellis notation • Color notation |
| MOS scales | Diamond-mos notation • KISS notation (Quasi-diatonic MOS notation) |
| Temperaments | Circle-of-fifths notation • Ups and downs notation (alternative symbols) • Syntonic–rastmic subchroma notation • Extended meantone notation • Fractional sharp notation |
See musical notation for a longer list of systems by category. See Category:Notation for the most complete, comprehensive list, but not sorted by category. | |